By Anna Lisa Ramella, Mario Schmidt (Poject C06 “Testing Futures”) and Megan A. Styles (University of Illinois Springfield)
Abstract
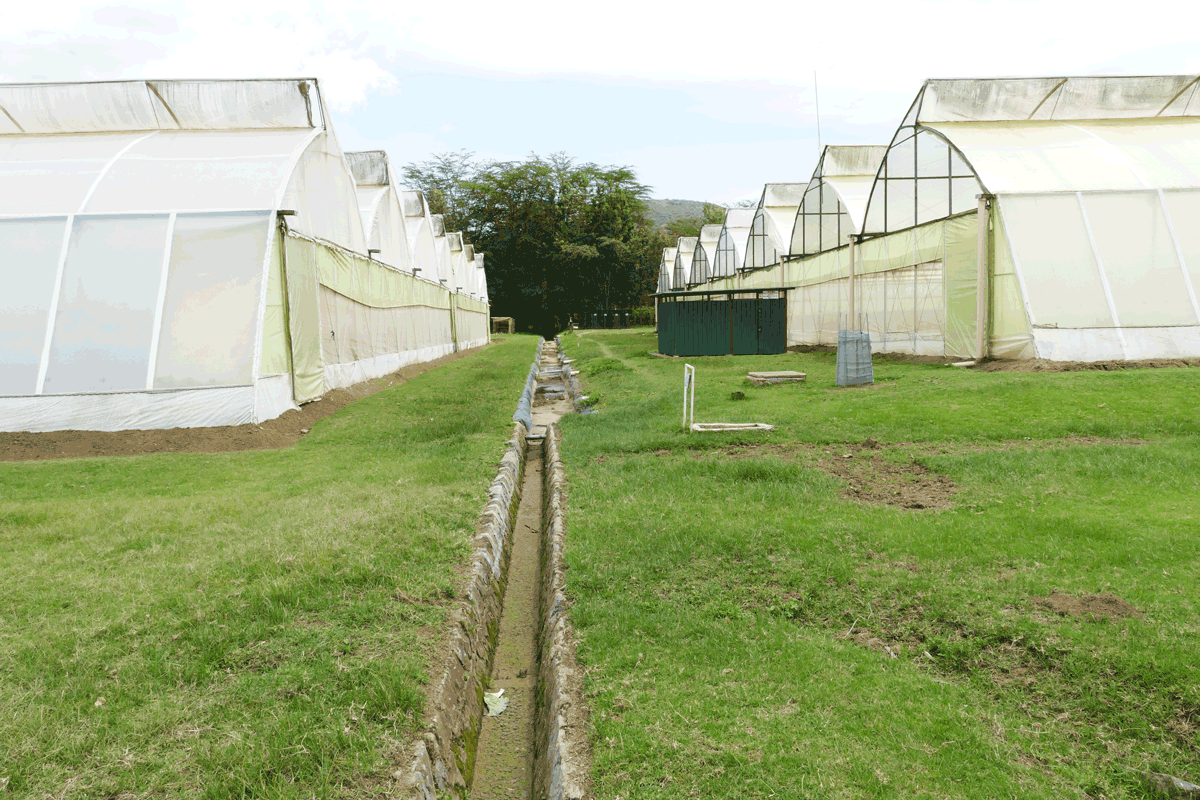
This article focuses on the financial collapse of and the subsequent interplay between material deterioration and maintenance on a flower farm in Naivasha that was placed under receivership in 2014. Our research is based on ethnographic fieldwork conducted by the three authors before, during, and after the farm’s collapse. We examine how laid-off workers, current employees, owners, and new management engage in a process we call ‘suspending ruination’, in which the farm is neither left to collapse nor fully restored to its original state. Maintaining the farm’s infrastructure creates a state of suspension characterised by opaque messages of potential – a process reinforced by both the receivers’ intent to resell the property, as well as the former employees’ anticipation of receiving outstanding compensations. Examining how their practices of caring for what appears to be a ‘ruin’ uphold the farm as an ambiguous object of capitalist potential, our article complements ongoing research on ruinations, instigated by capitalism’s future-making agendas.
Reference
Ramella, A.L., Schmidt, M. & Styles, M. 2023. Suspending ruination: preserving the ambiguous potentials of a Kenyan flower farm, Journal of Eastern African Studies, Full Text