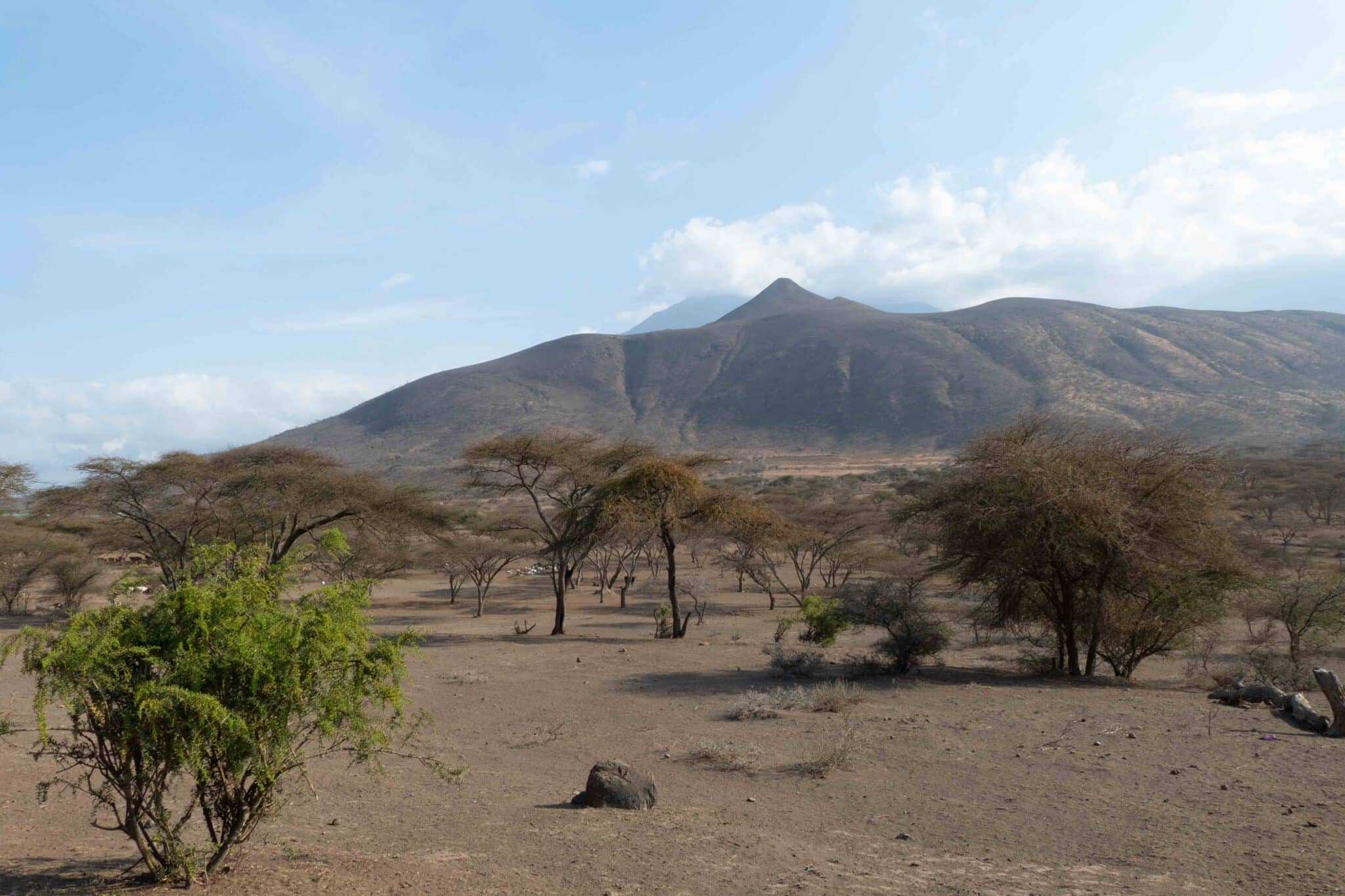
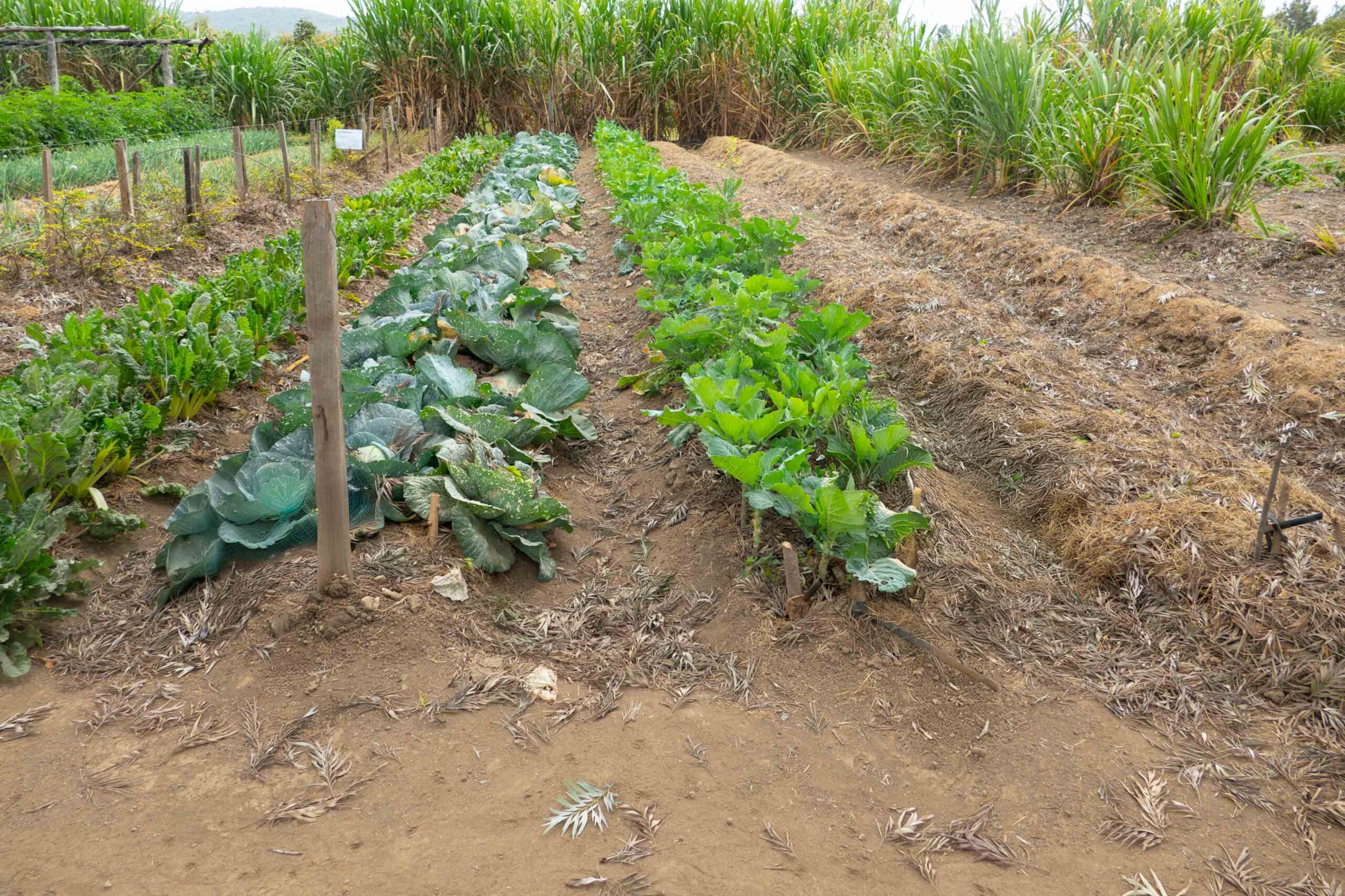
In a large-scale international study under leadership of the French research organizations INRAE/CNRS and the King Abdullah University in Saudi Arabia, scientists from 27 countries investigated how plants found in drylands have adapted to these extreme habitats. Their results published in “Nature” show a variety of plant adaptation strategies and an unexpected diversity increase with aridity levels. Scientists from the University of Potsdam participated in the study. The publication is co-authored by Liana Kindermann and Anja Linstädter (Project A01 Future Carbon Storage).
Abstract
Earth harbours an extraordinary plant phenotypic diversity that is at risk from ongoing global changes. However, it remains unknown how increasing aridity and livestock grazing pressure—two major drivers of global change—shape the trait covariation that underlies plant phenotypic diversity. Here we assessed how covariation among 20 chemical and morphological traits responds to aridity and grazing pressure within global drylands. Our analysis involved 133,769 trait measurements spanning 1,347 observations of 301 perennial plant species surveyed across 326 plots from 6 continents. Crossing an aridity threshold of approximately 0.7 (close to the transition between semi-arid and arid zones) led to an unexpected 88% increase in trait diversity. This threshold appeared in the presence of grazers, and moved toward lower aridity levels with increasing grazing pressure. Moreover, 57% of observed trait diversity occurred only in the most arid and grazed drylands, highlighting the phenotypic uniqueness of these extreme environments. Our work indicates that drylands act as a global reservoir of plant phenotypic diversity and challenge the pervasive view that harsh environmental conditions reduce plant trait diversity. They also highlight that many alternative strategies may enable plants to cope with increases in environmental stress induced by climate change and land-use intensification.
Reference
Gross, N., Maestre, F.T., Liancourt, P., Kindermann, L., Linstädter, A. et al. 2024. Unforeseen plant phenotypic diversity in a dry and grazed world. Nature (2024). DOI