In this recent publication, Future Rural Africa reseachers Alexandra Sandhage-Hofmann, Lydia Chabala, Chizumba Shepande and Wulf Amelung (Project A01 Future Carbon Storage) collaborate with Felicidade Jorge, Nkumbu Mutwale, Melanie Braun from The Institute of Crop Science and Resource Conservation of the University of Bonn, Armindo Cambule, Alfredo Nhantumbo and Sá Lisboa from Eduardo Mondlane University Mozambique, Benson Chishala from the University of Zambia, M. Matangue from the Polytechnic Institute of Gaza, Mozambique and Michael Schmidt from the University of Bonn’s Center for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces.
Abstract
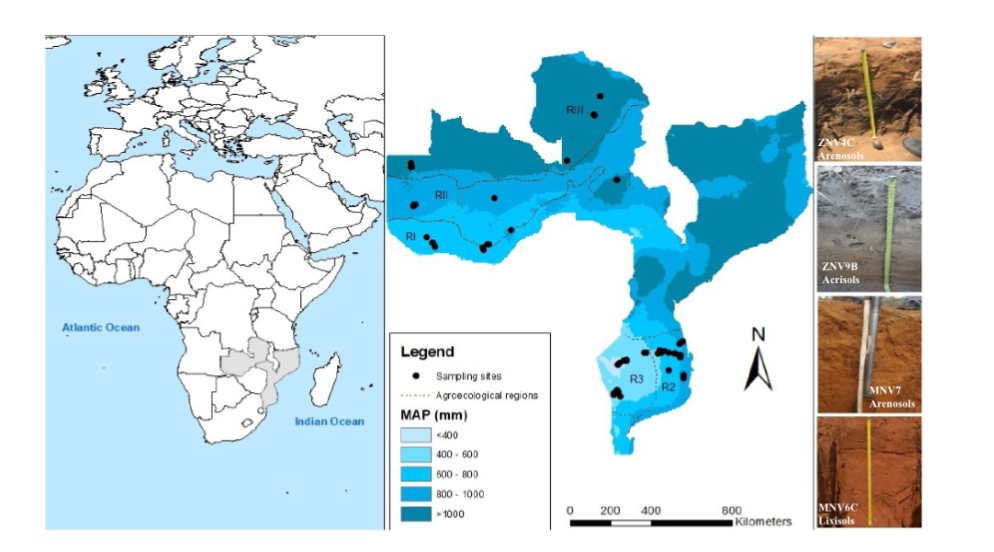
Savanna ecosystems in sub-Saharan Africa harbor substantial yet relatively unexplored reserves of soil organic carbon (SOC). Our study unravels for the first time the interplay between climate, reference soil groups, and anthropogenic disturbances in shaping SOC dynamics in these ecosystems. We analyzed SOC along climosequences in natural woodlands in Mozambique and Zambia, with mean annual temperature (MAT) of 20–24°C, and mean annual precipitation (MAP) of 365–1,227 mm. Anthropogenic disturbances were assessed through comprehensive field surveys and remote sensing of vegetation and indices change. MAT and evapotranspiration (PET) had no discernible effect on SOC. Bulk SOC, particulate organic matter, and mineral-associated organic matter stocks in the topsoil (0–10 cm) increased with MAP, though this relationship was not significant for the subsoil. MAP explained only 35% of topsoil SOC variability, limited by anthropogenic disturbances, which raised SOC stocks in the dry savanna but resulted in SOC losses at >600 mm MAP, which even extended into subsoil. For sites with little disturbance in the past decades, there were soil group-specific effects of MAP on SOC, explaining up to 85% of data variability. In disturbed sites, human presence altered the carbon (C) balance to an extent that, as rough estimate, could account for up to 2.6 Gt CO2-C loss over 20 years in wetter sites, with another 2.4 Gt CO2-C at risk as populations spread into these otherwise pristine environments. Accurate modeling of climate-change effects on the C cycle must therefore include the transformative impacts of current human activities, such as wood harvesting and grazing.
Key Points:
- Mean annual precipitation is the major driver of topsoil soil organic carbon (SOC) storage in savanna woodlands, not subsoil, and only at low-disturbed sites
- Human presence-induced SOC losses in the wetter savanna, overriding the influence of precipitation in the native savanna
- There was no significant effect of anthropogenic disturbance on SOC loss in the dry parts of the savanna
Reference
Jorge, J. F., Mutwale-Mutale, N., Sandhage-Hofmann, A., Braun, M., Cambule, A., Nhantumbo, A., Chabala, L. M., Shepande, C., Chishala, B., Lisboa, S., Matangue, M., Schmidt, M., Amelung, W. 2025. Anthropogenic disturbances superimpose climate effects on soil organic carbon in savanna woodlands of sub-Saharan Africa. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 39, DOI