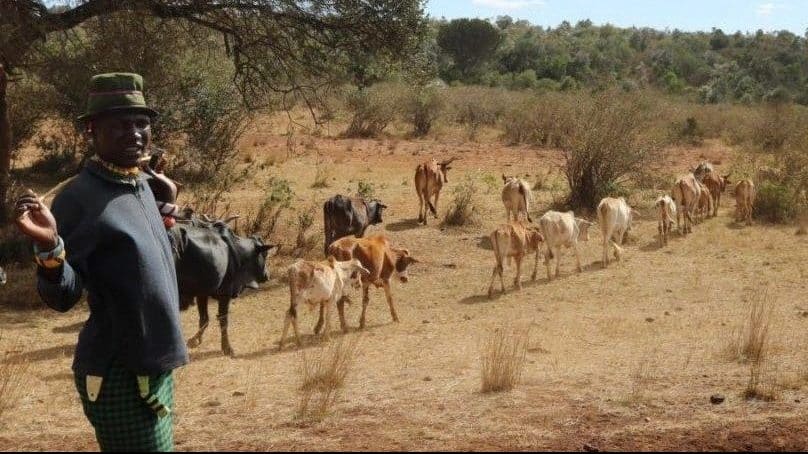
Parallel to a worldwide trend, the community-based conservation model is an increasing phenomenon in Kenya, especially in northern pastoralist counties. Publication author of BICC Working Paper 3\\2020, Kennedy Mkutu considers dimensions of inclusion and exclusion and subsequent conflicts around community-based conservancies in Isiolo County.
Currently, conservancies occupy an area larger than all national parks and have some of the largest numbers of wildlife in Kenya. They may be privately or government-owned or, most commonly, established on areas of communally-owned land and run by a board of community representatives. Several conservancies in Kenya are set up on the land of former ranches owned by settler families who continue to be important players in the sector. As conservancies serve to protect wildlife, an objective which the state supports, the state allocates armed rangers and arms for privately employed rangers for protection. Conservancies may provide a platform and an incentive for peacebuilding activities, but at the same time, they introduce new dimensions of exclusion and subsequent conflicts in the local society. Based on the results of empirical research over several years, the author comes to the following main findings:
- Community-based conservancies have the potential to empower local communities and increase their participation in conservation.
- Within conservancies, there are dimensions of spatial and political exclusion for members.
-
Conservancies introduce new dimensions of spatial exclusion on their boundaries and subsequent local conflicts in society.
-
The lines between defence and aggression are sometimes blurred for conservancy rangers.
-
The presence of conservancy security can inadvertently create power imbalances between historical rivals on conservancy borders, as well as arms races. That a non-state body receiving outside donor funding has an influential role in the management of conservancy security forces poses several dilemmas and has implications for sustainability and state sovereignty. There is a risk that well-trained security personnel could pose a danger to the country.
This article has been lifted from BICC Working Paper 3\\2020 the complete paper, “Security dynamics in concervancies in Kenya: The case of Isiolo County”.